The next to post in the blog will be Tanner.
Friday, 30 September 2011
Mid-Chapter Review
The next to post in the blog will be Tanner.
Monday, 26 September 2011
Angles Formed by Parallel Lines
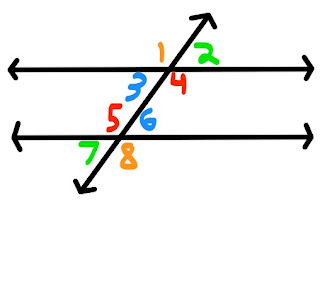
We started off class by looking over our Chapter 2 diagnostic work sheet and correcting a classmates to show Mr.Banow our knowledge in this unit so far.
Converse is a statement that is formed by switching the premise and the conclusion of another statement.
Next we worked on page 72 which is reviewing parallel lines and transversals.
We reviewed what Alternate Interior and Exterior angles were.
Alternate interior angles are two non-adjacent interior angles on opposite sides of a transversal. Which is angles 3,6 and 4,5.
Alternate exterior angles are two exterior angles formed between two lines and a transversal, on opposite sides of the transversal. Which is angles 1,8 and 2,7.
We also reviewed what Supplementary and Complementary angles were. Two angles are Supplementary angles if they add up to 180 degrees. These two angles (140 degrees and 40 degrees) are Supplementary Angles, because they add up to 180 degrees. These two angles (40 degrees and 50 degrees) are Complementary Angles, because they add up to 90 degrees.
The next person to blog will be, AARON. :)
OH YAH, and don't forget to bring a compass, protractor and ruler ASAP.
Exploring Parallel Lines
Our class did a hand out assignment on this and then we went over all the answers as a class and i believe it went very well because our class is very smart.
Next will be michelle :)
Friday, 23 September 2011
properties of angles and triangles. :)
we worked on a sheet to test our knowledge about triangles and angles and then worked on a dog activity on page 68. Most groups failed at the objective of making a dog using polygons.
this is all.
peeace.
next is............. cody. :)
Sunday, 18 September 2011
Analyzing Puzzles and Games
In summary: Both inductive and deductive reasoning can be useful for determining a strategy to solve a puzzle or win a game. Inductive reasoning is useful when analyzing games and puzzles that require recognizing patterns or creating a particular order. Deductive reasoning is useful when analyzing games and puzzles that require inquiry and discovery to complete.
we ended class with an assignment on page 55. #5,6,7,9,11
Next post will be from Amy! yay!
Thursday, 15 September 2011
1.6 Recap & 1.7: Analyzing Puzzles and Games

Wednesday, 14 September 2011
Reasoning To Solve Problems
To improve problem solving it would help to understand inductive and deductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning is based on facts that lead to a logical explanation, where as inductive reasoning is based on simple patterns to try and solve the problem.
Example of a deductive problem:
Mammals have hair. Dogs are mammals. So therefore, dogs have hair.
Conclusion:
Based on the statement, the answer is deductive because it demonstrates proof in the original statement.
Mammals have hair. (Which is all mammals, not just dogs)
Dogs are mammals. (Mammals have hair)
So we can come to the conclusion that, yes, all dogs have hair because there are mammals. There is proof stated, so the answer cannot be inductive, the statement is deductive.
- Next is Alex :)
Tuesday, 13 September 2011
SEPT 13
summary:
a single error in reasoningwill break down the logical argument of a deductive proof. this will result in an invalid conclusion, of a conclusion that is not supported buy the proof.
trying to divide by 0 will always cause a proof to be wrong, leading to an conclusion that is also wrong. also try avoid circular reasoning. when you write a proof try to keep is that it don't take a rocket scientist to make sense of it.
an example of to days work:
identify the error: all squares have 4 right angels. Quadrilateral PQRS has 4 right angels. therefore, PQRS is a square.
answer: not true quadrilateral PQRS could be a rectangle
Next is Joel
